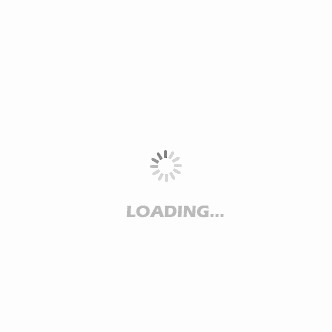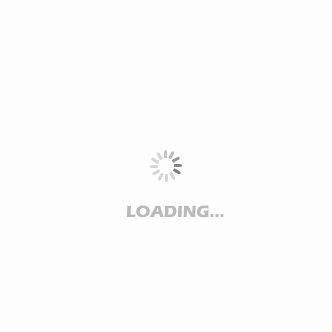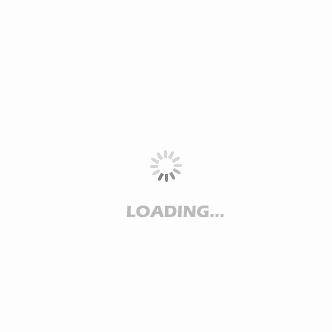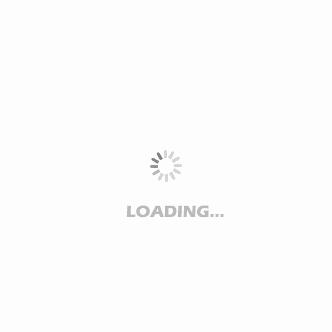
"Cheap rarpezit 250 mg fast delivery, bacteria from bees possible alternative to antibiotics".
By: K. Flint, M.A.S., M.D.
Assistant Professor, CUNY School of Medicine
It is closely associated with chronic active gastritis antibiotic tendon rupture discount 250 mg rarpezit fast delivery, peptic ulcer disease (gastric and duodenal ulcers) antibiotics quizlet generic rarpezit 250mg without a prescription, gastric cancer and gastric B cell lymphoma virus 0f2490 generic rarpezit 250 mg on line. Epidemiology Infection is acquired in childhood and persists for life unless treated. Infection is associated with lower socioeconomic status and is commoner in developing countries. In some individuals gastritis can involve the body of the stomach, leading to atrophic gastritis and in some cases intestinal metaplasia, which is a premalignant condition. Diagnosis of infection this is by non-invasive (serology, breath test or stool antigen) or invasive (antral biopsy for patients undergoing an endoscopy) tests (Table 3. It is also indicated for individuals who have a first-degree relative with gastric cancer. They are more common in the elderly, and there is a significant geographical variation. Clinical features Burning epigastric pain is the most common presenting symptom, typically relieved by antacids and a variable relationship to food. Occasionally ulcers may present with the complications of perforation or painless haemorrhage. Investigations Patients less than 55 years with ulcer-type symptoms should undergo noninvasive testing for H. Eradication is confirmed by either a urea breath test or faecal antigen testing in patients who remain symptomatic or who have had an ulcer complication. Conservative treatment with intravenous fluids and antibiotics may be indicated in elderly or very ill patients. Gastric outlet obstruction Ulcer disease causing obstruction is now rare and carcinoma is the commonest cause. Outflow obstruction occurs because of surrounding oedema or scarring following healing. Copious projectile vomiting is the main symptom, and a succussion splash may be detectable clinically. Management of dyspepsia Significant gastrointestinal pathology is uncommon in most young people with dyspepsia (p. These drugs deplete mucosal prostaglandins, by inhibiting the cyclo-oxygenase pathway, which leads to mucosal damage. Symptoms include indigestion, vomiting and haemorrhage, although these correlate poorly with endoscopic and pathological findings. Erosions (superficial breaks in the mucosa <3 mm) and subepithelial haemorrhage are most commonly seen at endoscopy. Other causes are autoimmune gastritis (the cause of pernicious anaemia associated with antibodies to gastric parietal cells and intrinsic factor), viruses and duodenogastric reflux. Gastritis is a histological diagnosis and is usually discovered incidentally when a gastric mucosal biopsy is taken for histology at endoscopy. Acute inflammation is associated with neutrophilic infiltration, while chronic inflammation is characterized by mononuclear cells, chiefly lymphocytes, plasma cells and macrophages.
Drug concentration in plasma does not correlate with therapeutic effect and monitoring is only necessary to assess complications of suspected toxicity treatment for dogs chocolate order discount rarpezit on-line. Monitor liver biochemistry 6-monthly in those most at risk of severe liver damage (check with British National Formulary) antibiotic juice recipe buy rarpezit cheap online. Many drug interactions with antiepileptics and other drugs (check with British National Formulary) antibiotic resistant bacteria uti purchase discount rarpezit line. Phenytoin Mechanism of action Inhibits sodium influx across the cell membrane, reduces cell excitability. Indications All forms of epilepsy except absence seizures, but used much less in developed countries. Other side effects are dose related and include impaired brainstem and cerebellar function (nystagmus, double vision, vertigo, ataxia, dysarthria), chronic connective tissue effects (gum hyperplasia, coarsening of facial features, hirsutism), skin rashes (withdraw treatment), folate deficiency, increased vitamin D metabolism and deficiency, blood dyscrasias, lymphadenopathy and teratogenic effects. Cautions/contraindications Contraindicated in sinus bradycardia, heart block and porphyria. Highly protein bound and can be displaced by valproate and salicylates, which therefore enhance the effect. Induction of hepatic drug-metabolizing enzymes and metabolism of warfarin and ciclosporin increased (see British National Formulary for full list). Pro-drug of phenytoin which can be given more rapidly and causes fewer infusion site reactions. There are over 1000 different entities described, but two-thirds of all cases are the result of fewer than 10 conditions. In developing countries, infectious diseases such as tuberculosis, leprosy and onchocerciasis are common, whereas in developed countries, inflammatory disorders such as acne and eczema are common. The majority are caused by the Gram-positive cocci Staphylococcus aureus (part of the normal microflora of the skin) and Streptococcus pyogenes. Sometimes infection is introduced by an animal bite or a penetrating foreign body and in these cases more unusual organisms can be found. Cellulitis is a spreading infection involving the deep subcutaneous layer and is the most common skin infection leading to hospitalization. It falls into a continuum of skin infections that includes impetigo (superficial vesiculopustular infection in children), folliculitis (multiple erythematous lesions with a central pustule localized to the hair follicles) and carbuncles (abscesses in the subcutaneous tissue that drain via hair follicles). Cellulitis preferentially involves the lower extremities, while erysipelas tends to affect the face. It is usually caused by a streptococcus, rarely a staphylococcus, and sometimes community acquired methicillin-resistant S. Clinical features Cellulitis presents as erythema in the involved area, with poorly demarcated margins, swelling, warmth and tenderness. In erysipelas the area is raised and erythematous and sharply demarcated from normal skin. In the majority of cases, culturing blood or skin aspirates does not reveal a pathogen. Treatment Treatment is with flucloxacillin (or erythromycin if penicillin allergic).
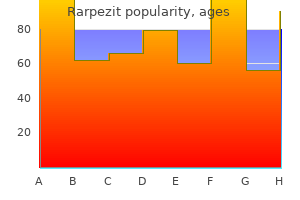
Certain ultrasonographic features have been identified that may suggest an increased risk for malignancy such as hypoechogenicity antibiotics sinus infection npr buy rarpezit mastercard, the presence of microcalcifications antimicrobial resistance global report on surveillance buy discount rarpezit line, increased central blood flow antibiotic 875125 cheap generic rarpezit canada, or irregular borders. However, in the absence of the aforementioned features, malignancy cannot be excluded definitively. The major role of thyroid scintigraphy is to determine the functional status of a suspected autonomously functioning thyroid nodule. Osteomyelitis of vertebra Vertebral osteomyelitis should be considered in all patients experiencing unremitting and/or focal vertebral pain that is not relieved by lying down, particularly if accompanied by fever or paravertebral symptoms indicating a psoas or other paraspinal extension. Radiography should be ordered for all patients with suspected vertebral osteomyelitis. The earliest signs are loss of definition of a vertebral end plate and narrowing of the associated disc space. If radiography is not diagnostic and the patient has pain that is unremitting or if patient is febrile, other imaging should be considered. Cystic hygroma Cystic hygroma is a type of congenital lymphatic malformation most commonly seen in the pediatric age group. It is an endothelial lined cavernous lymphatic space arising from the expansion of embryonic lymph lakes that fails to develop normal lymphatic drainage. They may show variable density/intensity, with a combination of fluid, soft tissue, and fat. Other common head and neck lesions Second branchial cleft cyst Embryologic cysts derived from second branchial apparatus typically present as a rounded cystic mass just below the angle of mandible, anterior to the sternocleidomastoid (Figure 8. This chapter will discuss the role of the different imaging modalities in the evaluation of the musculoskeletal system, the normal appearance of musculoskeletal specific structures, and the critical concepts in the analysis of musculoskeletal examinations. Brief overviews of trauma, arthritis, tumors, and interventional procedures will follow. Imaging modalities radiography Radiographs of biological tissues result in four densities: air, fat, soft tissue, and bone. The variation in soft tissue density between that of water, blood, muscle, and other organs is so small that these cannot be differentiated on a radiograph. Many structures in the extremities are bordered by fat, allowing one to identify normal contours. Radiography is particularly suited to imaging bones for two reasons: the very large difference in density between the bone and soft tissue and their high spatial resolution. Radiographs are the mainstay for the imaging of the arthritides, the initial assessment of bone tumors, the evaluation of orthopedic instrumentation, and, of course, trauma. Due to the relatively low cost of radiographs and wide availability, radiographs serve as the initial diagnostic study for all musculoskeletal complaints. Limitations of radiography include limited ability to evaluate complex threedimensional structures (such as the cervical spine, the sacroiliac joints, and the complex fractures), limited ability to penetrate large volumes of tissue, and quite limited ability to evaluate soft tissue pathology. Routine diagnostic radiographic examinations have at least two (anteroposterior and lateral) and often more projections that are tailored to the body part in question. The tangential patellar view (or "sunrise view") of the knee, the mortise view of the ankle, and the outlet view of the shoulder are examples. By convention, dense structures (such as bone) are bright on radiographs, whereas less dense structures (such as air) are dark. The primary use of fluoroscopy in musculoskeletal radiology is to guide needles for joint injections/aspirations and bone biopsies. Fluoroscopy is often used intraoperatively to guide and/ or evaluate the placement of orthopedic instrumentation. By convention, fluoroscopic images are displayed such that dense structures are dark compared to less dense structures, which are bright-the inverse of the radiographic convention.
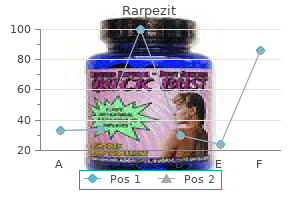
On longterm follow-up bacteria life cycle discount rarpezit online mastercard, some patients develop autoimmune diseases or severe infections [11] antibiotic resistance cdc purchase 100 mg rarpezit with visa. Germinal centers in lymphadenopathy associated with drug hypersensitivity are commonly enlarged with numerous centroblasts and tingible body macrophages oral antibiotics for acne while pregnant buy cheap rarpezit 100 mg on line. The variable clinical picture of drug-induced hypersensitivity syndrome/drug rash with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms in relation to the eliciting drug. Short- and long-term outcomes of 34 patients with drug-induced hypersensitivity syndrome in a single institution. Amyloidosis Lymphadenopathy 38 Amyloidosis lymphadenopathy involves deposition of amyloid of any type in lymph node(s). Amyloid is a pathologic extracellular protein with a characteristic cross -pleated structure whose accumulation causes widespread parenchymal organ damage. The secreted protein is ingested by macrophages, processed, and subsequently discharged into the extracellular matrix. A summary of the most common types of amyloid and their associated clinical manifestations is summarized in Table 38. Amyloid deposits are located around blood vessels in the earlier phases of the disease but form coalescent sheets as the disease advances. Amyloidosis involving lymph nodes also can be identified in fine needle aspiration cytology material [16]. The Congo red stain is traditionally the first step in recognizing the presence of amyloid deposits. With the Congo red stain, all forms of amyloid exhibit orange-red staining by routine light microscopy, with a characteristic apple-green birefringence when the tissue is visualized by using polarized light [17, 18]. Amyloidosis can be evaluated using immunohistochemistry, which is capable of distinguishing subtypes of the protein [19]. More recently, mass spectrometry-based proteomic analysis has been shown to be an excellent method for distinguishing various types of amyloid [20]. Nodular pulmonary amyloidosis is characterized by localized immunoglobulin deposition and is frequently associated with an indolent B-cell lymphoproliferative disorder. Primary amyloidosis involving mesenteric lymph nodes: diagnosis by fine-needle aspiration cytology. Incidence and natural history of primary systemic amyloidosis in Olmsted County, Minnesota, 1950 through 1989. A rare case of primary systemic amyloidosis of the neck with massive cervical lymph node involvement: a case report and review of the literature. The disease affects whites more often than other races, with a slight male predominance [4]. Extranodal sites of disease are also common, with bones and skin being two of the most common sites. Patients are most commonly young children, younger than 6 years old, who present with extranodal disease particularly involving skin, bone, and soft tissue [2, 3, 7, 8]. In the lymph node, involvement generally leads to complete effacement of nodal architecture.
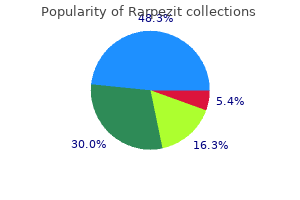
In the following discussion antibiotics you can't take while pregnant discount rarpezit 100 mg amex, lesions are separated as non-neoplastic and neoplastic bacteria discovery cheap rarpezit online visa. It is common to find lymphocyte depletion and atrophic follicles with progressive depletion of germinal centers virus 10 states purchase rarpezit 100mg without prescription. Secondary changes include follicular and interfollicular lymphoid hyperplasia and granulomatous inflammation that can be associated with infections. Histologically, lymphoid follicles lack germinal centers and there is an accumulation of IgM+ plasma cells in nodal and extranodal sites, the latter including the gastrointestinal tract, spleen, liver, and gallbladder. These lesions may not become clonal, but may cause massive organ enlargement and occasionally are fatal. Molecular studies may reveal transient clonal populations of B cells with V-J rearrangements. Findings include a systemic polymorphous proliferation of B-lymphocytes, plasmacytoid, and immunoblastic cells. Hemophagocytic syndrome is common in cases of fulminant infectious mononucleosis and is better seen in bone marrow aspirates. The most common histologic types are nonHodgkin lymphoma (50 %) diffuse large B-cell lymphoma, followed by Burkitt lymphoma, Hodgkin lymphoma (9 %) and peripheral T-cell lymphoma. More rarely, T-and B- lymphoblastic leukemia/lymphoma and T-cell prolymphocytic leukemia have been reported. Various patterns of viral latency may be observed, depending on the degree of immune competence of the host. Monotypic cytoplasmic immunoglobulin may be detected in cases with plasmacytic differentiation. Studies of clonality used for lymphoproliferative disorders in reactive and neoplastic processes apply for lymphoproliferative disorders associated with primary immune disorders. Therefore, the presence of clonal populations by molecular testing of antigen receptor genes of T- or B-cell lineage support the presence of a neoplastic clone, and this information requires integration with clinical and pathologic findings. These include breakpoints at 14q1112, 7q32-35, 7p15, inv(7)(p13q35), t(7;7)(p13q35), t(7;14) (p13;q11), t(14;14)(q11;q32), as well as the immunoglobulin genes. However, lymphoid proliferations in other primary immune disorders may be aggressive. In general, a conservative approach is recommended for self-limited or indolent cases. Prophylactic antibiotics and/or intravenous immunoglobulin reduce rates of infections and increase survival of patients with common variable immunodeficiency [17]. Hodgkin and non-Hodgkin lymphomas are treated with standard therapy used in immunocompetent patients with similar neoplasms. These features are morphologically suspicious of a lymphoma, thus extensive workup was performed in this lymph node, but no evidence of clonality by immunophenotypic or molecular studies were found. The presence of hyperplastic, although distorted, germinal centers hints that the molecular damage does not affect the formation of germinal center cells. Overview of lymphoproliferative disorders associated with primary immune deficiency disorders. Cancer risk among patients with IgA deficiency or common variable immunodeficiency and their relatives: a combined Danish and Swedish study. Patient-centred screening for primary immunodeficiency: a multi-stage diagnostic protocol designed for nonimmunologists.
Generic rarpezit 500 mg free shipping. Loads of areca nuts to be peeled.