"Order zitroneo with amex, antibiotics for uti that are safe during pregnancy".
By: Q. Marius, M.A., Ph.D.
Professor, Marist College
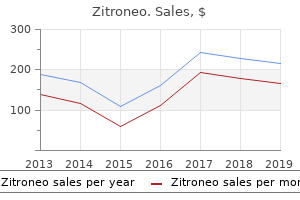
Apical alveoli are distended compared with basal alveoli at rest secondary to greater compressive force at the base of the lung antibiotics for face infection order cheap zitroneo online, as depicted by the three different alveolar positions at rest infection 2 hacked discount 250mg zitroneo. With inspiration virus 36 generic 250 mg zitroneo amex, the basal alveoli are exposed to greater ventilation, while the apical alveoli see minimal ventilation, as illustrated by the change in distention between the alveoli from rest to inspiration. Did You Know During spontaneous ventilation, both ventilation and perfusion are greater in gravitydependent areas. In the upright position, alveoli are resting at larger inflated volumes at the apex compared with the base of the lung secondary to greater compressing gravitational pressure outside the alveoli at the base. The alveoli at the base are relatively less inflated but resting at a more compliant position. As the lungs are inflated, the basal alveoli receive more ventilation because they are at a more compliant point than apical alveoli and the distending pressure is greater. Central regions of the lung are preferentially ventilated, but as flow rates are increased, this ventilatory difference is minimized. Simply stated, during spontaneous ventilation, more gas is distributed to gravity-dependent areas. Alveolar perfusion is also heterogeneous in the lung and dependent mainly upon gravity. Physiologically, the pulmonary artery pressure must always exceed pulmonary venous pressure; the zones are described by the degree of alveolar pressure in relation to pulmonary artery and venous pressure. Perfusion depends on the relative resistance to the pulmonary artery pressure in each of the zones. The pulmonary artery pressure is low enough that the alveolar pressure can result in pulmonary capillary compression, limiting perfusion. Fortunately, this zone comprises the majority of the lung, allowing for matching of perfusion and ventilation. Perfusion in zone 2 is determined by the relative pressure difference between pulmonary artery and alveolar pressure. In zone 3, perfusion depends on the pulmonary artery and venous pressure gradient. Ventilation and Perfusion Relationship Matching ventilation with perfusion is vital to ensuring carbon dioxide and oxygen gas exchange. Ideally, ventilation would be perfectly matched with perfusion, optimizing the possibility for gas diffusion across the alveolar and pulmonary capillary membranes. The distribution of ventilation and perfusion, however, is heterogeneous in the lung, resulting in mismatches of ventilation and perfusion. Perfusion Rate Ventilation Apex Lung location Base Figure 2-9 Ventilation perfusion matching. Both ventilation and perfusion of alveoli increase at the base compared with the apex, but the rate of increase is greater for perfusion than for ventilation, with progression to the base of the lung. Dead space is the portion of ventilation inadequately exposed to perfusion, primarily altering carbon dioxide elimination. Dead space can be absolute if the ventilation is exposed to no perfusion or relative when the ventilation is exposed to poor perfusion. Anatomical dead space, an absolute dead space, is the portion of ventilation to structures that are incapable of gas exchange, such as the pharynx, trachea, and large airways. Anatomically, ventilation must first supply anatomical dead space as it is a conduit for gas travel to the alveoli, resulting in an increased proportion of dead space ventilation with decreases in tidal volume. Alveolar dead space, which can be both absolute and relative, consists of ventilation to alveoli with suboptimal perfusion exposure.
When these mediators are released into the circulation antibiotics for acne after accutane generic zitroneo 100 mg otc, they are considered hormones antimicrobial 220 order 500mg zitroneo, because they are synthesized infection without antibiotics purchase zitroneo 500 mg on-line, stored, and released by the adrenal gland (4). Thus, the endogenous catecholamines are mainly inactivated by reuptake into the synapse. The liver and kidneys mainly metabolize the exogenous catecholamines, and this mechanism confers a longer duration of action. Afferent impulses are integrated centrally and sent reflexively to the adrenergic and cholinergic receptors. Its stimulation induces bradycardia, bronchoconstriction, miosis, salivation, and increased gastrointestinal motility. M1 receptors are found in the autonomic ganglia and in the gastric parietal cells; M2 receptors are mainly located at the heart; and M3 receptors are located at the smooth muscle level. If the nicotine dose is increased further, the symptoms become those of hypotension and neuromuscular weakness, as it becomes an inhibitor instead. Recently another category, a 3 receptor present in the adipose tissue, was identified as well. Classically, the 1 receptors are located in the smooth muscle of the peripheral vessels, coronary arteries, skin, uterus, intestinal mucosa, and splanchnic beds. The effect in vessels is vasoconstriction, while on the intestinal tract its effect is relaxation. There is evidence that there are 1 receptors within the myocardium, such that using 1-adrenergic antagonists can provide antiarrhythmic effects. The postsynaptic 2 are responsible for vasoconstriction, platelet aggregation, inhibition of insulin release, and bowel motility as well as the release of the antidiuretic hormone. The 2 receptors are predominant in the smooth muscle of the blood vessels, the skin, muscles, mesentery, and bronchial tree. Did You Know In general, the number of adrenergic receptors is inversely proportional to the concentration of circulating catecholamines. The number of receptors fluctuates depending on physiologic, genetic, and developmental factors. Receptors are produced by the sarcoplasmic reticulum and are externalized to the synaptic membrane. Catecholamines induce a direct effect on the number or the concentration of the receptors, which is termed upregulation or downregulation, and these can be altered by changing or discontinuing the administration of adrenergic drugs. Autonomic Nervous System Reflexes When the autonomic pathways are disrupted due to a variety of pathologic conditions, loss of normal function is expected. One example is Horner syndrome, which is associated with ptosis, myosis, and anhydrosis (eyelid droop, inability to increase the diameter of the pupil, and inability to sweat, respectively), which is determined by disruption of the respective sympathetic pathways. Tests that are used to determine autonomic dysfunction include monitoring of cardiac parameters during changes in posture (tilt table test), cold pressor test (hand immersion in ice-cold water), Valsalva maneuver, and even nerve conduction studies monitoring sweating and thermal changes. The most common feature of autonomic dysfunction is orthostatic hypotension with a decrease of at least 20 mm Hg in systolic blood pressure or a decrease of 10 mm Hg Did You Know Orthostatic hypotension is a harbinger of an increase in perioperative morbidity and mortality and should be considered an additional risk factor for a given patient. Valsalva maneuver requires forced expiration against resistance, which has the purpose of decreasing the venous blood return into the thorax, with a subsequent decrease in the blood pressure. A normal response is sensed by the baroreceptors and a reflex increase in the heart rate that is sympathetically mediated should be expected. On the other hand, patients with dysautonomia will not have the expected increase in the heart rate. An 80-year-old female received midazolam 2 mg for premedication for an uneventful 30-minute gynecologic procedure (propofol infusion and fentanyl).
Zitroneo 500 mg lowest price. Sentinel Formula 539 Smoke & Odor Encapsulant - Jon-Don Video.
Postoperative nausea and vomiting is more common with etomidate than with propofol or thiopental and it lacks any analgesic properties antibiotic resistance china buy genuine zitroneo line. Etomidate transiently inhibits 11-hydroxlase antibiotic resistance and meat order genuine zitroneo on line, an enzyme involved in the production of steroids infection simulator cheap zitroneo line, which causes adrenocortical suppression. In its favor, however, etomidate does not cause histamine release and causes minimal hemodynamic depression and bronchoconstriction, even in the presence of cardiovascular and pulmonary disease. It is this hemodynamic stability that underlies the continued use of etomidate in clinical practice. Did You Know Unlike propofol and the barbiturates, sedation with benzodiazepines can be pharmacologi cally reversed with flumazenil, a specific competitive antagonist for benzodiazepines. Did You Know Etomidate transiently inhibits 11hydroxlase, an enzyme involved in the production of steroids, even after a single induction dose. Terminal elimination occurs by hepatic biotransformation to inactive metabolites that are then renally excreted. Of the two forms, S+ ketamine is more potent than the R- stereoisomer and exhibits a greater rate of clearance and a faster recovery from anesthesia (7). Ketamine has unique properties to distinguish it from other intravenous anesthetics: it stimulates the sympathetic nervous system, has minimal respiratory depression, and it causes potent bronchodilation. Ketamine has several routes of administration, making it an excellent choice for uncooperative patients and pediatrics. Ketamine causes analgesia not only by blocking the pain signal at the spinal cord but also by "disassociating" the communication of pain between the thalamus and limbic system. This state of dissociative amnesia causes the patient to appear conscious (eyes open, staring) but remain unresponsive to sensory input (pain, verbal stimulus). In isolation, ketamine is a direct myocardial depressant, but secondary to this indirect release of catecholamines, it acts as a cardiac stimulant, causing increased blood pressure, heart rate, and cardiac output. Some caution is required in patients with pre-existing sympathetic blockade, such as those with spinal cord lesions or those with exhaustion of their catecholamine stores. Termination of the clinical effect of ketamine is primarily due to redistribution from the brain to the peripheral tissues. Ketamine is hepatically metabolized by the cytochrome P450 system into several metabolites, of which one, norketamine, retains some anesthetic properties. Although lipid soluble, ketamine is the least protein-bound molecule of all intravenous anesthetics. However, patients who are at risk for aspiration should be intubated during general anesthesia with ketamine. Ketamine causes increased lacrimation and salivation that may lead to laryngospasm. Pretreatment with an anticholinergic agent such as glycopyrrolate can attenuate this response. Unfortunately, ketamine tends to produce unpleasant emergence reactions such as hallucinations, out of body experiences, and fear, which have limited its widespread use as a primary anesthetic medication. These emergence reactions are better tolerated in the pediatric population and should be of major consideration in psychiatric patients. Nevertheless, the unique properties of ketamine and its multiple documented routes of administration (intravenous, intramuscular, oral, rectal, and even epidural and intrathecal) give it many adjunct clinical uses. Dexmedetomidine Dexmedetomidine (Precedex) is the S-enantiomer of medetomidine and is a centrally-acting, highly-selective 2 agonist. The 2 receptors are located presynaptically and in the locus ceruleus, an area of brain responsible for arousal and sympathetic activity. The 2 receptors are inhibitory receptors and, when activated, decrease the amount of downstream neurotransmitter released. For sympathetic nerves, this results in less catecholamine release, which causes decreased blood pressure and heart rate.
Vasopressin Vasopressin (antidiuretic hormone) is a peptide hormone released from the posterior pituitary that regulates water reabsorption in the kidney and exerts potent hemodynamic effects independent of adrenergic receptors antibiotics for urine/kidney infection purchase zitroneo 100mg with amex. Vasopressin receptors consist of three subtypes (V1 antibiotic 7 days buy zitroneo 500mg amex, V2 antibiotics buy online quality zitroneo 100 mg, and V3), all of which are fivesubunit helical membrane proteins coupled to G proteins. Activation of the V1 receptor subtype stimulates phospholipase C and triggers hydrolysis of inositol 4,5-bisphosphate to inositol 1,4,5-triphosphate and diacylglyercol. These second messengers increase intracellular Ca2+ concentration and produce contraction of the vascular smooth muscle cell. V2 receptors are present on renal collecting duct cells, and, when activated, increase reabsorption of free water, whereas the more recently described V3 receptors are located in the pituitary. Indeed, exogenous administration 13 Cardiovascular Pharmacology 245 of vasopressin has been shown to effectively support arterial pressure when a relative vasopressin deficiency exists. Intraoperative hypotension that is relatively refractory to administration of catecholamines or sympathomimetics has been repeatedly described in patients who have been treated with these medications. General or neuraxial anesthesia also reduces sympathetic nervous system tone, resulting in decreased plasma stress hormone concentrations including vasopressin. Under these circumstances, administration of vasopressin activates V1 vascular smooth muscle receptors and rapidly increases arterial pressure during anesthesia by causing arterial vasoconstriction. Vasopressin therapy has been shown to reduce mortality associated with acute vasodilatory states such as anaphylaxis. In addition, infusion of vasopressin is indicated for the treatment of severe hypotension after prolonged cardiopulmonary bypass in patients who are otherwise unresponsive to phenylephrine or norepinephrine (vasoplegia). Vasodilation that is refractory to fluid resuscitation combined with a relative deficiency of endogenous vasopressin is a characteristic feature of sepsis. Administration of vasopressin in the absence or presence of other vasoactive medications often improves hemodynamics and facilitates survival in patients with sepsis. The combined use of vasopressin with other vasoactive medications often reduces the overall dose of vasopressin required to maintain arterial pressure, thereby limiting the adverse effects of vasopressin on organ perfusion. In fact, sustained administration of higher doses of vasopressin may produce mesenteric ischemia, peripheral vascular insufficiency, and cardiac arrest because the drug causes pronounced vasoconstriction of cutaneous, skeletal muscle, splanchnic, and coronary vascular beds concomitant with reduced perfusion of and oxygen delivery to these tissues. Bolus intravenous administration of vasopressin is also used as part of the advanced cardiac life support algorithm for cardiac arrest resulting from ventricular fibrillation, pulseless electrical activity, and asystole. Beta-Blockers Many of the cardiovascular actions of b adrenoceptor antagonists (beta-blockers) may be anticipated based on the previous discussion of catecholamines. Indeed, beta-blockers have been repeatedly shown to reduce mortality and morbidity associated with myocardial infarction in a number of large clinical trials. The most recent American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association guidelines recommend continuation of beta-blockers in patients who are receiving them chronically for established cardiac indications. Beta-blocker initiation should be considered for vascular surgery patients and other patients at high risk of myocardial ischemia who are scheduled to undergo intermediate- or high-risk noncardiac surgery (Table 13. Perioperative beta-blocker therapy should 246 Clinical Anesthesia Fundamentals Table 13-4 Recommendations for Perioperative Beta-Blocker Therapy 2009 Perioperative Focused Update Recommendations 1. Beta blockers should be given to patients undergoing vascular surgery who are at high cardiac risk owing to the finding of ischemia on preoperative testing. Beta blockers are probably recommended for patients undergoing vascular surgery in whom preoperative assessment identifies coronary heart disease.