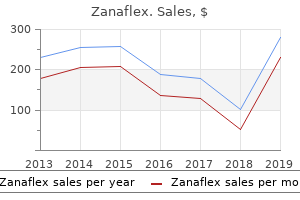
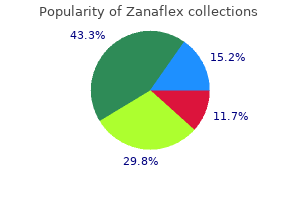
"Purchase zanaflex 4mg amex, spasms throughout body".
By: U. Larson, M.S., Ph.D.
Clinical Director, Dartmouth College Geisel School of Medicine
Efficacy of buccal midazolam compared to intravenous diazepam in controlling convulsions in children: a randomized controlled trial muscle relaxant yellow house order zanaflex with a visa. Current status of the 1 muscle relaxant clonazepam discount 4 mg zanaflex,4- and 1 muscle relaxant voltaren purchase zanaflex 2 mg on-line,5-benzodiazepines in the treatment of epilepsy: the place of clobazam. The cognitive and behavioral effects of clobazam and standard monotherapy are comparable. Sugai K Clobazam as a new antiepileptic drug and clorazepate dipotassium as an alternative antiepileptic drug in Japan. Side effects of carbamazepine, valproate and clonazepam during long-term treatment of epilepsy. Treatment of status epilepticus with a new benzodiazepine more active than diazepam. Treatment of status epilepticus: a prospective comparison of diazepam and phenytoin versus phenobarbital and optional phenytoin. Respiratory depression in children receiving diazepam for acute seizures: a prospective study. Adverse reactions to intravenous diazepam: a report from the Boston Collaborative Drug Surveillance Program. Relationship between diazepam dose, plasma level, age, and central nervous system depression. Clinical toxicity of chlordiazepoxide and diazepam in relation to serum albumin concentration: a report from the Boston Collaborative Drug Surveillance Program. Tonic status epilepticus precipitated by intravenous diazepam in a child with petit mal status. Pain following intravenous administration of sedative agents: a comparison of propofol with three benzodiazepines. Extravasation of phenytoin and diazepam requiring surgical debridement and skin grafting. Incidence and extent of venous sequelae with intravenous diazepam utilizing a standardized conscious sedation technique. The effects of intravenous lorazepam alone and with meperidine on ventilation in man. Comparison of lorazepam alone vs lorazepam, morphine, and perphenazine for cardiac premedication. Sequelae after the intravenous injection of three benzodiazepines: diazepam, lorazepam, and flunitrazepam. Results of studies in animal models of epilepsy and seizures indicate that brivaracetam has higher potency than levetiracetam, and a potential for superior efficacy across a broad range of seizure types [3]. Chemistry Brivaracetam [2S]-2-[(4R)-2-oxo-4-propylpyrrolidinyl]butanamide is a 2-pyrrolidone derivative, freely soluble in water, with a molecular weight of 212 [2]. Brivaracetam showed higher efficacy and potency than levetiracetam in these models [3]. The increase in population spike amplitude induced by bicuculline methiodide was inhibited by brivaracetam at concentrations as low as 0. Brivaracetam shows potent seizure protection in many in vivo models of seizures and epilepsy (Table 31. Unlike levetiracetam, brivaracetam is effective in inhibiting seizures induced in the classic maximal electroshock and pentylenetetrazole seizure tests, albeit at fairly high doses.
Therefore muscle relaxant addiction purchase zanaflex 4 mg on line, monitoring ethosuximide concentrations is usually not necessary spasms hiatal hernia purchase generic zanaflex, but it may be useful in selected cases spasms movie cheap 2mg zanaflex with visa, such as patients who failed to respond to the drug or patients with suspected adverse effects. It also has other Phenytoin acts as a voltage-dependent sodium channel blocker [30]. Both the rate and extent of phenytoin absorption from the gastrointestinal tract can vary across formulations. The plasma protein binding of the drug is approximately 90%, but the unbound fraction may increase in patients with hypoalbuminemia, renal failure or comedication with drugs such as valproic acid which displace phenytoin from plasma protein binding sites [41]. As a result, the pharmacokinetics of phenytoin is non-linear and small increments in dosage can result in disproportionately large increments in serum phenytoin concentration (Figure 10. Interactions affecting phenytoin pharmacokinetics occur rather frequently, resulting in decrease or, more often, increases in serum phenytoin concentration (see Chapter 43). In situations where the unbound fraction is increased, therapeutic and toxic effects are expected to occur at concentrations lower than in patients with unaltered plasma protein binding. This is not only because of the relatively good relationship between serum concentration and clinical effects, but Pharmacokinetic Optimization of Therapy 133 also because of the extreme pharmacokinetic variability and, most importantly, the non-linear relationship between serum concentration and dosage. Because small changes in phenytoin dosage can produce disproportionately large changes in steady-state serum drug concentration, particularly when the latter is near or above the lower limit of the reference range, knowledge of the serum concentration is very important in deciding the magnitude of dosage adjustments [1,47]. Second generation antiepileptic drugs Felbamate Primidone Primidone differs from phenobarbital in lacking a carbonyl group. Although it has an anticonvulsant action on its own, its effects are primarily mediated by metabolically derived phenobarbital. The conversion of primidone to phenobarbital can be affected by drug interactions, and the elimination of phenobarbital itself can be affected by a number of concomitantly administered drugs [39]. However, the value of monitoring serum primidone concentrations in the routine setting is not clearly established, and in most cases it is sufficient to monitor the serum concentration of metabolically derived phenobarbital. The use of felbamate today is greatly restricted because of the risk of aplastic anaemia and liver toxicity. The clearance of felbamate is considerably higher in children than in adults [23]. About 50% of a given dose is metabolized in the liver to metabolites devoid of antiseizure activity, and there is some evidence that intermediate reactive metabolites such as atropaldehyde can be responsible for the serious hepatic and haematological toxicity of the drug [52]. Valproic acid Valproic acid is a short-chain branched fatty acid, the mechanisms of antiseizure action of which have not been clearly elucidated. Valproic acid is well absorbed after oral administration, but the absorption profile differs markedly in relation to the formulation used (see Chapter 51). The unbound fraction of valproic acid is also increased in patients with renal disease, chronic liver disease, pregnancy and other conditions associated with low albumin concentrations [5,48].
Purchase 4mg zanaflex fast delivery. NECK AND THROAT RELAXATION EXERCISES (5 of 6) -- Vocal Exercises -- American English Pronunciation.
Caffeine withdrawal headaches are also common because of the large amount of caffeine consumed in coffee spasms of pain from stones in the kidney order 4mg zanaflex free shipping, various soft drinks spasms pregnancy buy zanaflex 4mg fast delivery, and chocolate infantile spasms 4 months discount zanaflex online visa. Drugs that may induce headache include the nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs such as indomethacin (Indocin) and the antihypertensives such as clonidine, aspirin, quinidine, and bromides. Trauma may cause concussion and postconcussion headaches, intracranial neoplasms such as subdural hematoma, and cervical sprain, all of which can induce headaches. It should be taken seriously because it may mean a subarachnoid hemorrhage or meningitis. Chronic headaches, on the other hand, are most likely due either to migraine if they occur in exacerbations or remissions, or to tension headaches if they are fairly constant, mild, and chronic. The headache of a brain tumor is rarely severe and is rarely the presenting symptom of a brain tumor. Headaches that occur in clusters almost daily for 6 to 8 weeks with interruptions of several months must make one consider cluster headaches. The presence of nuchal rigidity should make one think of a subarachnoid hemorrhage or meningitis, but it may also be due to cerebral hemorrhage or cerebral abscess. If the headache is associated with fever, the possibility of acute sinusitis should be considered, and the sinuses should be transilluminated. Other sources of the fever should be looked for, and meningitis or encephalitis should be considered. With acute headache and focal neurologic signs and/or papilledema, one should consider cerebral abscess or cerebral hemorrhage. With a chronic headache and papilledema or focal neurologic signs, one should consider a space-occupying lesion such as a primary brain tumor or metastatic neoplasm. A sinus transilluminator should be in the armamentarium of every physician who expects to diagnose headache. If the sinuses fail to transilluminate, one should consider acute sinusitis as the diagnosis. The presence of a tender superficial temporal artery should make one think of temporal arteritis, particularly in the elderly, but it may also be related to a long-standing migraine attack. Relief of the headache on superficial temporal artery compression should suggest classical or common migraine. If one can relieve the headache by compression of the occipital artery, occipital migraine should be considered. When there is no relief on compression of the superficial temporal artery, one should consider tension headaches, occipital neuralgia, cervical spondylosis, and cluster headaches as the cause. A chest x-ray should also be done to rule out the possibility of metastatic neoplasm. Visual acuity should always be evaluated because chronic headache is often due to a refractive error or astigmatism. If there are focal neurologic signs, referral should be made to a neurologist or neurosurgeon as soon as possible. It is usually best to refer the patient to a neurologist or neurosurgeon if there is nuchal rigidity. If the headaches are chronic and episodic, and there are no focal neurologic signs, papilledema, or nuchal rigidity, an imaging study can be postponed for a while until the response to treatment is evaluated. Difficult cases of headache should also be studied with 24-hour blood pressure monitoring, a 24-hour urine for catecholamines, and lumbar puncture to diagnose central nervous system lues.
Cerebral blood flow is greatly increased and Other drug therapies Clonazepam is an alternative benzodiazepine which has a long history of use as emergency therapy in acute seizures zma muscle relaxant order cheap zanaflex. Indeed muscle relaxant in surgeries generic zanaflex 2 mg fast delivery, when introduced in 1975 spasms sphincter of oddi generic 4mg zanaflex, it was considered by Gastaut to be superior to diazepam [2] and it is still the therapy favoured in France. However, there is a scarcity of published data on its effectiveness [87,88] and no controlled studies. Nevertheless, it has a longer redistribution half-life than diazepam and so there are theoretical reasons to favour its use. Rectal paraldehyde is another long-used alternative therapy, which is undoubtedly highly effective and safe, and it still retains 230 Chapter 17 thus glucose delivery to active cerebral tissue is maintained [96]. Acidosis also commonly occurs, and in one series 25% of the patients had an arterial pH below 7. This acidosis is mainly the result of lactic acid production, but there is also a rise in carbon dioxide tension that can, in itself, result in life-threatening narcosis [99]. The acidosis can increase the likelihood of life-threatening cardiac arrhythmias and hypotension and, in conjunction with the cardiovascular compromise, may result in severe pulmonary oedema [100]. The status epilepticus then enters a second phase in which cerebral and systemic protective measures progressively fail. The main characteristics of this phase are a fall in blood pressure, a loss of cerebral autoregulation, resulting in the dependence of cerebral blood flow on systemic blood pressure, and hypoglycaemia due to the exhaustion of glycogen stores and the increased neurogenic insulin secretion [94,101,102]. The combined effects of systemic hypotension and intracranial hypertension can result in a compromised cerebral circulation and cerebral oedema [103], particularly in children. Further complications may occur, including rhabdomyolysis, leading to acute tubular necrosis, hyperkalaemia and hyponatraemia [104]. If there is a history of alcoholism, or other compromised nutritional states, 250 mg thiamine. This is particularly important if glucose has been administered, as a glucose infusion increases the risk of Wernicke encephalopathy in susceptible patients. Routine glucose administration in non-hypoglycaemic patients should be avoided as there is some evidence that this can aggravate neuronal damage. Acidosis If acidosis is severe, the administration of bicarbonate has been advocated in the hope of preventing shock, and mitigating the effects of hypotension and low cerebral blood flow. In most cases, however, this is unnecessary and more effective is the rapid control of respiration and abolition of motor seizure activity. Establish aetiology the causes of status epilepticus differ with age, and in the presence or absence of established epilepsy. If the status epilepticus has been precipitated by drug withdrawal, the immediate restitution of the withdrawn drug, even at lower doses, will usually rapidly terminate the status epilepticus. Pyridoxine should also be given intravenously to children under the age of 3 years who have a prior history of epilepsy and to all neonates. Physiological changes and medical complications the physiological changes of uncompensated status epilepticus may need specific therapy.