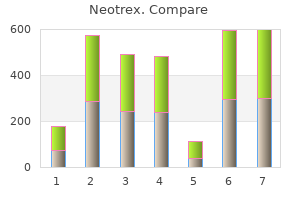
"Discount 40mg neotrex with mastercard, skin care coconut oil".
By: E. Chris, M.A.S., M.D.
Medical Instructor, University of Toledo College of Medicine
The radial styloid process can be easily palpated in the anatomical snuff box on the lateral side of the wrist skin care physicians discount neotrex line. Because the process extends more distally than the ulnar styloid process skin care tips in urdu purchase neotrex paypal, more ulnar deviation than radial deviation of the wrist is possible skin care videos 10 mg neotrex sale. The relationship of the radial and ulnar styloid processes is important in the diagnosis of certain wrist injuries. Proximal to the radial styloid process, the anterior, lateral, and posterior surfaces of the radius are palpable for several centimeters. The dorsal tubercle of radius is easily felt around the middle of the dorsal aspect of the distal end of the radius. The dorsal tubercle acts as a pulley for the long extensor tendon of the thumb, which passes medial to it. The pisiform can be felt on the anterior aspect of the medial border of the wrist and can be moved from side to side when the hand is relaxed. The hook of the hamate can be palpated on deep pressure over the medial side of the palm, approximately 2 cm distal and lateral to the pisiform. The tubercles of the scaphoid and trapezium can be palpated at the base and medial aspect of the thenar eminence (ball of thumb) when the hand is extended. The metacarpals, although overlain by the long extensor tendons of the digits, can be palpated on the dorsum of the hand. The heads of these bones form the knuckles of the fist; the 3rd metacarpal head is most prominent. The knuckles of the fingers are formed by the heads of the proximal and middle phalanges. Because the disabling effects of an injury to an upper limb, particularly the hand, are far out of proportion to the extent of the injury, a sound understanding of the structure and function of the upper limb is of the highest importance. Knowledge of its structure without an understanding of its functions is almost useless clinically because the aim of treating an injured limb is to preserve or restore its functions. Clavicular fractures are especially common in children, and are often caused by an indirect force transmitted from an outstretched hand through the bones of the forearm and arm to the shoulder during a fall. The weakest part of the clavicle is the junction of its middle and lateral thirds. After fracture of the clavicle, the sternocleidomastoid muscle elevates the medial fragment of bone. Because of the subcutaneous position of the clavicle, the end of the superiorly directed fragment is prominent-readily palpable and/or apparent. The trapezius muscle is unable to hold the lateral fragment up owing to the weight of the upper limb; thus, the shoulder drops. In addition to being depressed, the lateral fragment of the clavicle may be pulled medially by the adductor muscles of the 421 arm, such as the pectoralis major. Slings are used to take the weight of the limb off the clavicle to facilitate alignment and the healing process. The slender clavicles of neonates may be fractured during delivery if they have broad shoulders; however, the bones usually heal quickly. A fracture of the clavicle is often incomplete in younger children-that is, it is a greenstick 422 fracture (see Fractures of Humerus in this clinical box). Ossification of Clavicle the clavicle is the first long bone to ossify (via intramembranous ossification), beginning during the 5th and 6th embryonic weeks from medial and lateral primary ossification centers that are close together in the shaft of the clavicle.
The fibrous layer has an opening or gap posterior to the lateral tibial condyle to allow the tendon of the popliteus to pass out of the joint capsule to attach to the tibia acne tretinoin cream 005 discount neotrex 5mg on line. Inferiorly acne off buy 5mg neotrex with mastercard, the fibrous layer attaches to the margin of the superior articular surface (tibial plateau) of the tibia acne 50 year old woman buy online neotrex, except where the tendon of the popliteus crosses the bone. The quadriceps tendon, patella, and patellar ligament replace the fibrous layer anteriorly-that is, the fibrous layer is continuous with the lateral and medial margins of these structures, and there is no separate fibrous layer in the region of these structures. Internal aspect of joint capsule of knee: layers, articular cavity, and articular surfaces. The joint capsule was incised transversely, the patella was sawn through, and then, the knee was flexed, opening the articular cavity. The 1801 infrapatellar fold of synovial membrane encloses the cruciate ligaments, excluding them from the joint cavity. All internal surfaces not covered with or made of articular cartilage (blue or gray in the case of the menisci) are lined with synovial membrane (mostly purple, but transparent and colorless where it is covering nonarticular surfaces of the femur). The attachments of the fibrous layer and synovial membrane to the tibia are shown. Note that although they are adjacent on each side, they part company centrally to accommodate intercondylar and infrapatellar structures that are intracapsular (inside the fibrous layer) but extra-articular (excluded from the articular cavity by synovial membrane). The extensive synovial membrane of the capsule lines all surfaces bounding the articular cavity (the space containing synovial fluid) not covered by articular cartilage. Thus, it attaches to the periphery of the articular cartilage covering the femoral and tibial condyles, the posterior surface of the patella, and the edges of the menisci, the fibrocartilaginous discs between the tibial and femoral articular surfaces. The synovial membrane lines the internal surface of the fibrous layer laterally and medially, but centrally, it becomes separated from the fibrous layer. From the posterior aspect of the joint, the synovial membrane reflects anteriorly into the intercondylar region, covering the cruciate ligaments and the infrapatellar fat pad, so that they are excluded from the articular cavity. This creates a median infrapatellar synovial fold, a vertical fold of synovial membrane that approaches the posterior aspect of the patella, occupying all but the most anterior part of the intercondylar region. Thus, it almost subdivides the articular cavity into right and left femorotibial articular cavities; indeed, this is how arthroscopic surgeons consider the articular cavity. Fat-filled lateral and medial alar folds cover the inner surface of fat pads that occupy the space on each side of the patellar ligament internal to the fibrous layer. Superior to the patella, the knee joint cavity extends deep to the vastus intermedius as the suprapatellar bursa. The synovial membrane of the joint capsule is continuous with the synovial lining of this bursa. This large bursa usually extends approximately 5 cm superior to the 1802 patella; however, it may extend halfway up the anterior aspect of the femur. Muscle slips deep to the vastus intermedius form the articularis genu, which attaches to the synovial membrane and retracts the bursa during extension of the knee. They are sometimes called external ligaments to differentiate them from internal ligaments, such as the cruciate ligaments. The patellar ligament, the distal part of the quadriceps femoris tendon, is a strong, thick fibrous band passing from the apex and adjoining margins of the patella to the tibial tuberosity. Laterally, it receives the medial and lateral patellar retinacula, aponeurotic expansions of the vastus medialis and lateralis and overlying deep fascia. The retinacula make up the joint capsule of the knee on each side of the patella.
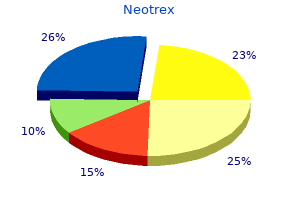
Buy discount neotrex 5 mg. Quotes my top 10 proverty quotes.
They participate in the formation of the peri-articular genicular anastomosis skin care malaysia discount neotrex 10mg with mastercard, a network of vessels surrounding the knee that provides collateral circulation capable of maintaining blood supply to the leg during full knee flexion acne y clima frio polar buy neotrex 30 mg fast delivery, which may kink the popliteal artery acne keloid treatment purchase neotrex 40 mg visa. Other contributors to this important genicular anastomosis are the descending genicular artery, a branch of the femoral artery, superomedially. Muscular branches of the popliteal artery supply the hamstring, gastrocnemius, soleus, and plantaris muscles. The superior muscular branches of the popliteal artery have clinically important anastomoses with the terminal part of the profunda femoris and gluteal arteries. The popliteal vein begins at the distal border of the popliteus as a continuation of the posterior tibial vein. Throughout its course, the vein lies close to the popliteal artery, lying superficial to it in the same fibrous sheath. The popliteal vein is initially posteromedial to the artery and lateral to the tibial nerve. More superiorly, the popliteal vein lies posterior to the artery, between this vessel and the overlying tibial nerve. Superiorly, the popliteal vein, which has several valves, becomes the femoral vein as it traverses the adductor hiatus. The small saphenous vein passes from the posterior aspect of the lateral malleolus to the popliteal fossa, where it pierces the deep popliteal fascia and enters the popliteal vein. The superficial popliteal lymph nodes are usually small and lie in the subcutaneous tissue. A lymph node lies at the termination of the small saphenous vein and receives lymph from the lymphatic vessels that accompany this vein. The deep popliteal lymph nodes surround the vessels and receive lymph from the joint capsule of the knee and the lymphatic vessels that accompany the deep veins of the leg. The lymphatic vessels from the popliteal lymph nodes follow the femoral vessels to the deep inguinal lymph nodes. The anterior (dorsiflexor or extensor) compartment contains four muscles (the fibularis tertius lies inferior to the level of this section). The posterior (plantarflexor or flexor) compartment, containing seven muscles, is subdivided by an intracompartmental transverse intermuscular septum into a superficial group of three (two of which are commonly tendinous/aponeurotic at this level) and a deep group of four. The popliteus (part of the deep group) lies superior to the level of this section. The anterior compartment of the leg, or dorsiflexor (extensor) compartment, is located anterior to the interosseous membrane, between the lateral surface of the shaft of the tibia and the medial surface of the shaft of the fibula. The anterior compartment is bounded anteriorly by the deep fascia of the leg and skin. The deep fascia overlying the anterior compartment is dense superiorly, providing part of the proximal attachment of the muscle immediately deep to it. With unyielding structures on three sides (the two bones and the interosseous membrane) and a dense fascia on the remaining side, the relatively small anterior compartment is especially confined and therefore most susceptible to compartment syndromes (see the clinical box "Containment and Spread of Compartmental Infections in the Leg"). Inferiorly, two band-like thickenings of the fascia form retinacula that bind the tendons of the anterior compartment muscles before and after they cross the ankle joint, preventing them from bowstringing anteriorly during dorsiflexion of the joint. These dissections demonstrate the continuation of the anterior and lateral leg muscles into the foot. The thinner portions of the deep fascia of the leg have been removed, leaving the thicker portions that make up the extensor and fibular retinacula, which retain the tendons as they cross the ankle. At the ankle, the vessels and the deep fibular nerve lie midway between the malleoli and between the tendons of the long dorsiflexors of the toes. Synovial sheaths surround the tendons as they pass beneath the retinacula of the ankle. The superior extensor retinaculum is a strong, broad band of deep fascia, passing from the fibula to the tibia, proximal to the malleoli.
Before birth skin care zinc generic 5 mg neotrex free shipping, the umbilical arteries are the main continuation of the internal iliac arteries skin care with ross order 30mg neotrex, passing along the lateral pelvic wall and then ascending the anterior abdominal wall to and through the umbilical ring into the umbilical cord skin care 90210 order neotrex 40 mg line. Prenatally, the umbilical arteries conduct oxygen- and nutrient-deficient blood to the placenta for replenishment. When the umbilical cord is cut, the distal parts of these vessels no longer function and become occluded distal to branches that pass to the bladder. The ligaments raise folds of peritoneum (medial umbilical folds) on the deep surface of the anterior abdominal wall (see Chapter 2, Back). Postnatally, the patent parts of the umbilical arteries run antero-inferiorly between the urinary bladder and the lateral wall of the pelvis. The origin of the obturator artery is variable; usually, it arises close to the origin of the umbilical artery, where it is crossed by the ureter. It runs antero-inferiorly on the obturator fascia on the lateral wall of the pelvis and passes between the obturator nerve and vein. Within the pelvis, the obturator artery gives off muscular branches, a nutrient artery to the ilium, and a pubic branch. It ascends on the pelvic surface of the pubis to anastomose with its fellow of the opposite side and the pubic branch of the inferior epigastric artery, a branch of the external iliac artery. In a common variation (20%), an aberrant or accessory obturator artery arises from the inferior epigastric artery and descends into the pelvis along the usual route of the pubic branch. The extrapelvic distribution of the obturator artery is described with the lower limb (Chapter 7). In females, it may occur-with nearly equal frequency-as a separate branch of the internal iliac artery or as a branch of the uterine artery. The uterine artery is an additional branch of the internal iliac artery in females, usually arising separately and directly from the internal iliac artery. It descends on the lateral wall of the pelvis, anterior to the internal iliac artery, 1344 and passes medially to reach the junction of the uterus and vagina, where the cervix (neck) of the uterus protrudes into the superior vagina. The relationship of ureter to artery is often remembered by the phrase "water (urine) passes under the bridge (uterine artery). On reaching the side of the cervix, the uterine artery divides into a smaller descending vaginal branch, which supplies the cervix and vagina, and a larger ascending branch, which runs along the lateral margin of the uterus, supplying it. The ascending branch bifurcates into ovarian and tubal branches, which continue to supply the medial ends of the ovary and uterine tube and anastomose with the ovarian and tubal branches of the ovarian artery. The origin of the arteries from the anterior division of the internal iliac artery and distribution to the uterus and vagina are shown. The anastomoses between the ovarian and tubal branches of the ovarian and uterine arteries and between the vaginal branch of the uterine artery and the vaginal artery provide potential pathways of collateral circulation. These communications occur, and the ascending branch courses, between the layers of the broad ligament. It often arises from the initial part of the uterine artery instead of arising directly from the anterior division. The vaginal artery supplies numerous 1345 branches to the anterior and posterior surfaces of the vagina. The middle rectal artery may arise independently from the internal iliac artery, or it may arise in common with the inferior vesical artery or the internal pudendal artery.